Prepopulate.conf¶
The Prepopulate plugin provides a system for automatically setting data in records during editing using display templates and Expressions. Common use cases include:
Replicating data between parent and child records in hierarchies or related records.
Generating formatted text values using several metadata values and, potentially, context-specific logic. (Formatting various field values into a bibliographic citation, for example)
Forcing one or more fields to default values based upon the value of another field.
Prepopulate applies configured rules to records as they are edited. Rule typically define a target to set a value for and a display template with which to generate the value. Templates are evaluated relative to the record being edited so all values accessible with respect to that record, including related records and parent and child records in hierarchies are available to the template. Rules may be constrained to apply to specific tables and, optionally, record types. Application of rules can be made contingent upon evaluation of an ../../reference/expressions (which can also reference all values accessible to the edited record) or the current status of the target metadata element.
It is also possible to configure rules that replicate relationships between records. As of version 1.8, Prepopulate may be configured to replicate between records container metadata elements in whole or in part.
Basic Setup¶
All configuration is made in the prepopulate.conf configuration file. The enabled directive governs whether Prepopulate is active or not. It must be set to a non-zero value for any Prepopulate-based actions to occur. Two other directives control which user actions trigger application of configured rules when Prepopulate is enabled:
prepopulate_fields_on_editwill cause rules to be applied whenever a record is opened in the editor.prepopulate_fields_on_savewill trigger application of rules whenever a record is saved.
For rules to be applied enabled and at least one of prepopulate_fields_on_edit and prepopulate_fields_on_save must be set.
The prepopulate_rules directive contains a dictionary of rules to apply. Each key is a unique alphanumeric identifier for a rule. The precise value is not critical, but it must be unique and should be meaningful. Corresponding values are dictionaries with keys and values defining rule behavior.
An example prepopulate_rules dictionary with a single rule with code test_rule is shown below:
prepopulate_rules = {
# -------------------
test_rule = {
# what types of records does this rule apply to?
table = ca_objects,
restrictToTypes = [artwork],
# mode determines handling of existing values in target element
# can be merge, overwrite, overwriteIfSet or addIfEmpty
# See the 'target' setting below
mode = addIfEmpty,
# What's the prepopulate target?
# This can be an intrinsic field, labels or an attribute.
#
# Note that if you want to target a List attribute, you have to
# provide a valid list item idno or id for that list as value!
#
target = ca_objects.title_notes,
# skip this rule if expression returns true
# available variable names are bundle names
skipIfExpression = ^ca_objects.idno =~ /test/,
# content to prepopulate
# (this is a display template evaluated against the current record)
template = ^ca_objects.preferred_labels (^ca_objects.idno),
}
# -------------------
}
This rule applies to object records (see the table setting) of type “artwork” (see restrictToTypes). When evaluated, it will fill the “title_notes” field (see target) with the object record’s preferred label and identifier, formatted with the identifier in parens (see template). The rule will be skipped if the object identifier contains the word “test” (see skipIfExpression) or of there is already a value in the “title_notes” field for the object (see mode).
Replicating relationships and containers¶
Most rules generate a text value using template and copy it to the target, subject to optional restrictions (mode, skipIfExpression, restrictToTypes, etc). It is also possible to replicate relationships in Prepopulate using the context directive. In this case, target is the type of relationship to replicate and context defines the source of the relationship. Possible contexts are “related”, “parent” or “children”.
An example configuration for replicating relationships using context follows:
related_entities = {
table = ca_objects,
# add relationships that do not already exist
mode = merge,
# copy all entities related to objects related to the target record
target = ca_entities,
context = related,
# copy only those entities related with the relationship type "artist"
restrictToRelationshipTypes = [artist],
# don't copy relationships with specified relationship type codes;
#excludeRelationshipTypes = [],
# copy only entities that are the type "individual"
restrictToRelatedTypes = [individual],
# don't copy relationships pointing to specified types
#excludeRelatedTypes = [],
# only consider "current" relationships – Eg. current storage location
currentOnly = 0,
}
The example above copies all entity relationships to entities of type “individual” on objects related to the currently edited object. If the context had been set to “parent” entity relationships on the parent object would have been copied to the currently edited object.
Individual values in a container metadata element can be copied using the standard template/target rules described earlier. To copy an entire container between records without requiring a separate rule for each sub-element use the source directive to specify the container you wish to copy to the target. Prepopulate will assume the source and target containers have identical structure. To map values between different structures use the sourceMap directive to create a conversion table mapping equivalent sub-elements in each container.
An example configuration for replicating container values in their entirety from a parent record to a child record using source and sourceMap is below:
dimensions_container_rule = {
table = ca_objects,
restrictToTypes = [edition_item],
mode = addIfEmpty,
target = ca_objects.edition_dimensions,
# skip this rule if expression returns true
# available variable names are bundle names
#skipIfExpression = ^ca_objects.idno =~ /test/,
# for prepopulation of full containers where the container has the same
# format in both the source and target you can copy it directly by specifying
# a "source" specification. Sub-element codes must match exactly for this to work.
source = ca_objects.parent.edition_dimensions,
# If sub-element codes don't match exactly you can specify a mapping where source
# keys are on the left and target keys on the right. This also enables partial copy
# of containers, as when sourceMap is specified only those keys defined in the map are copied
sourceMap = {
edition_display_dimensions = edition_display_dimensions,
edition_dimensions_height = edition_dimensions_height,
edition_dimensions_width = edition_dimensions_width,
edition_dimension_types = edition_dimension_types,
edition_dimensions_notes = edition_dimensions_notes
},
omitFromIsSetCheck = [edition_dimension_types]
}
When determining if a container is empty or not (when mode is addIfEmpty), each element in the container will be checked. If any element contains a non-empty value the container will be considered populated. If the container includes elements that are never empty (Eg. drop-down lists with default values) then it may be necessary to skip consideration of those elements to make an accurate determination. As of version 1.8, the omitFromIsSetCheck option may be set to a list of element codes to skip. In the example above, edition_dimension_types is not checked when determining if the target container has existing values.
Settings¶
The following settings are available when configuring Prepopulate rules:
Setting name |
Description |
Valid values |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
table |
Defines what table the rule applies to. Required. |
Any primary table |
ca_objects |
restrictToTypes |
Optional list of types to restrict rule to. |
Any valid type for the table. |
[artwork, image] |
mode |
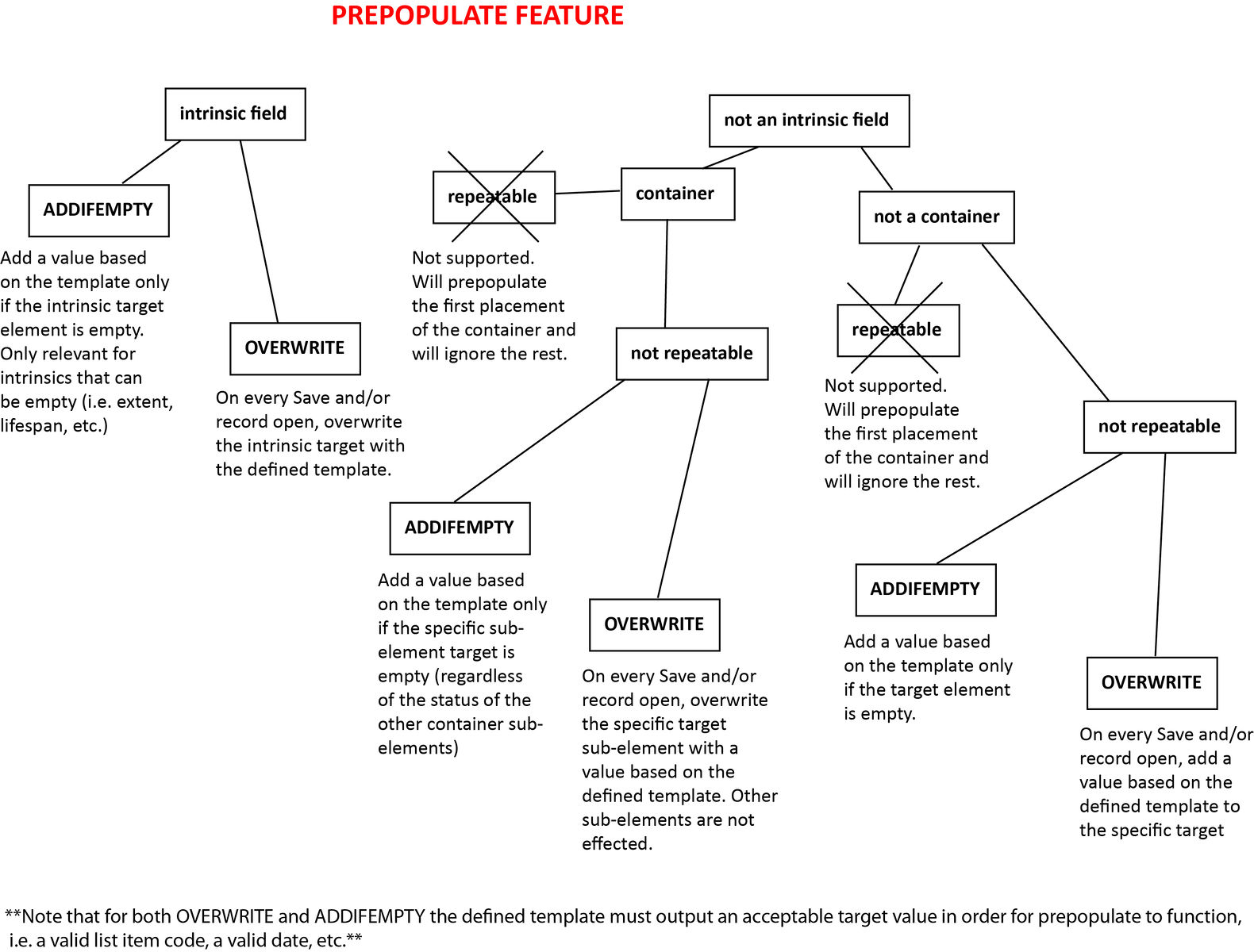
Required setting controlling how and if rule is applied when the target contains existing values. See flowchart below. Options are: addIfEmpty: set value only if none already exists overwrite: replace existing values; if the value to be set in the target is empty existing values will be removed but not replaced overwriteifset: replace existing values only if the value to be set to a non-empty value merge: add values that do not already exist |
One of addIfEmpty, overwrite, overwriteifset, merge |
addIfEmpty |
target |
Specifies the metadata element that the rule will set values for. The target must be part of the record being edited. The value set is defined by the template or source directives. Note that if when targetting a List metadata element, you must provide a valid list item idno or numeric item_id as the value. |
A valid bundle specifier for either a intrinsic field, labels or an metadata element |
[ca_objects.description] |
template |
A display template defining the value to be set in the target. The display template is evaluated against the current record and can incorporate any value accessible to the currently edited record, including related records and hierarchical values. Required, unless the rule is targeting a container metadata element with a full copy of another container in which case |
A valid display template. |
^ca_objects.medium_container.medium ^ca_objects.medium_container.support |
source |
Rules using |
A valid bundle specifier for a container metadata element. |
ca_objects.dimensions |
sourceMap |
A dictionary mapping sub-element codes in a source container (specified by the |
A dictionary container keys set to source container sub-element codes and values set to target sub-element codes. |
{ edition_display_dimensions = edition_display_dimensions, edition_dimensions_height = edition_dimensions_height, edition_dimensions_width = edition_dimensions_width, edition_dimension_types = edition_dimension_types, edition_dimensions_notes = edition_dimensions_notes } |
omitFromIsSetCheck |
A list of container elements to skip values checks for when determining if the target container already contains a value |
A list of element codes |
[edition_dimension_types] |
skipIfExpression |
An optional expression that controls if the rule is applied. The expression is evaluated relative to the currently edited record. If the result is true, the rule will not be applied for the current record. |
A valid expression |
^ca_objects.object_status_new !~ /deaccessioned/ |
context |
Controls how relationships are prepopulated. Options include parent = copy relationships from the parent record children = copy relationships from child records related = copy relationships from related records (Eg. if table = ca_objects and target = ca_entities copy all entity relationships from related objects) |
parent, children, or related |
parent |
restrictToRelationshipTypes |
When |
A list of valid relationship types |
[author, editor] |
excludeRelationshipTypes |
When |
A list of valid relationship types |
[creator] |
restrictToRelatedTypes |
When |
A list of valid types |
[artwork] |
excludeRelatedTypes |
When |
A list of valid types |
[ephemera, books] |
currentOnly |
When the |
1 or 0 |
0 |
Flowchart¶
Typical Prepopulate processes are diagrammed below. Note that the mode “overwriteifset” (which is not shown in the diagram) is identical to “overwrite,” save that no overwrite is performed for empty values.